Blog Details

3D-Printed Orthopaedic Implants: The Future of Personalized Surgery
Our approach to treatment, recuperation, and quality of life has always been altered by developments in medical technology. The incorporation of 3D printing into surgical implants is among the most innovative developments in contemporary orthopaedics. Orthopaedic implants have historically been mass-produced, made to fit a variety of patients, and infrequently tailored to each patient's unique anatomy. However, this is quickly changing today. Experts Dr. Rakesh Mahajan at Mahajan Clinic are leading the charge to introduce cutting-edge orthopaedic solutions like 3D-printed implants, giving patients hope for a future in which implants are customized to meet their individual requirements.
The Evolution of Orthopaedic Implants
Orthopaedic implants have long been used to replace worn-out joints, repair fractures, and increase mobility. Despite their great effectiveness, traditional implants frequently have drawbacks like poor fit, rejection risk, or the requirement for extra surgical adjustments.
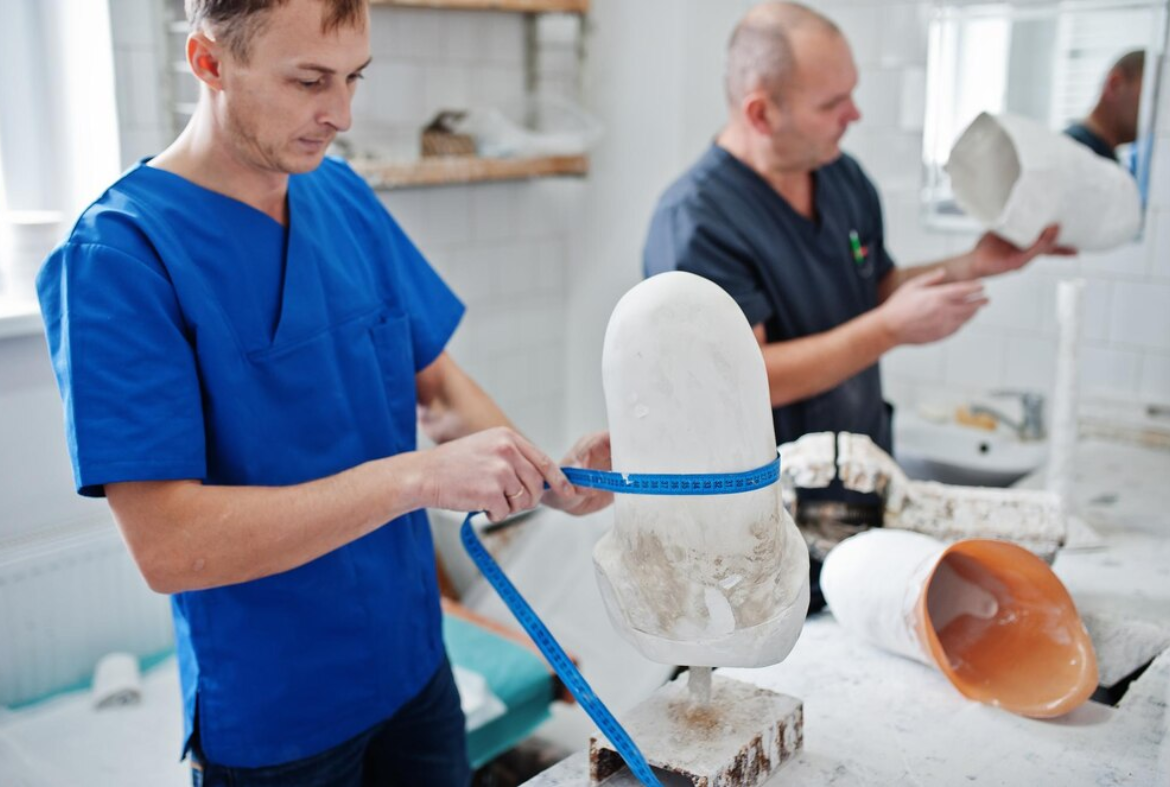
This is where additive manufacturing, commonly referred to as 3D printing, comes into play. Surgeons can create implants that precisely match a patient's bone structure by layering them together using cutting-edge biomaterials. This degree of personalization is a significant step in enhancing results and forming the future of orthopaedic implants.
Why 3D Printing Matters in Orthopaedics
The use of 3D-printed implants is a revolutionary development rather than merely a passing fad. This is the reason:
- Personalized Fit: Using information from MRIs or CT scans, each implant can be customized to a person's anatomy. For instance, a hip replacement can be made to precisely match the patient's original joint's dimensions and shape.
- Faster Recovery: An improved fit for an implant lessens the strain on the tissues around it. This improves post-operative comfort, reduces recovery time, and minimizes complications.
- Durability and Strength: Biocompatible metals like titanium and cobalt-chromium alloys, which are robust enough to withstand physical strain and prolonged use, are used in modern 3D printers.
- Complex Designs: The form and structure of implants are frequently constrained by conventional techniques. Surgeons can improve integration by using 3D printing to produce porous structures that promote the growth of natural bone around the implant.
- Cost Efficiency in the Long Run: Over time, 3D-printed implants become more cost-effective due to their quicker recovery and decreased need for revision surgeries, even though their initial costs may be higher.
Because of these advantages, a lot of experts think 3D printing is essential to the future of orthopaedic implants.
Applications of 3D-Printed Implants
3D printing is already being used in orthopaedics in a number of fields, including:
- Joint Replacements: Among the most popular replacements that benefit from customization are the hips, knees, and shoulders. Exact joint surfaces and angles can be replicated by 3D-printed implants.
- Spinal Surgery: By precisely matching the structure of the spine, surgeons can design implants that increase stability and lessen stress.
- Trauma Surgery: Customized plates, screws, or bone scaffolds can be made to fit odd breaks or bone loss in cases of complex fractures.
- Paediatric Orthopaedics: 3D printing enables more flexible solutions for developing kids that can be modified as they get older.
A new level of care is made possible by the accuracy and versatility of 3D-printed implants, underscoring their indisputable contribution to the future of orthopaedic implants.
Challenges to Overcome
Despite the enormous potential, there are still obstacles in the way of fully implementing 3D-printed orthopaedic implants in clinical settings:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Strict safety testing and approvals are necessary because implants are placed directly into the body.
- Costs of Technology: Although the cost of biocompatible materials and advanced printers is still high, it is anticipated that costs will decrease as use grows.
- Surgeon Training: To plan and perform procedures involving customized implants, surgeons require specific training.
- Long-Term Data: Long-term data on patient outcomes and durability are still being gathered because the technology is still in its infancy.
The future appears bright despite these obstacles, as ongoing advancements bring 3D-printed implants one step closer to becoming the norm.
The Patient Perspective
Personalization is the most exciting feature of this innovation for patients. One size no longer fits all. Rather, 3D printing guarantees that implants are made to fit their unique body, way of life, and even future mobility requirements. Longer-lasting implants and an enhanced quality of life may soon be available to patients who previously underwent numerous revision surgeries.
Additionally, pre-surgical models are made possible by 3D printing. In order to improve planning and minimize surprises in the operating room, surgeons can print models of a patient's bone or joint prior to surgery. This enhances accuracy, security, and patient trust.
Collaborative and Global Impact
The effects are not limited to the operating room either. More collaborative care is becoming possible thanks to 3D-printed orthopaedic implants. In order to ensure that implants are not only anatomically correct but also optimized for long-term function, engineers, biomedical scientists, and surgeons now collaborate during the design phase. As they examine digital models and comprehend how their personalized implant will enhance their quality of life, patients are becoming more and more involved in these conversations. This open, collaborative method lowers preoperative anxiety while increasing trust between the patient and the physician.
Additionally, because of 3D printing's versatility, quick prototypes can be made in a matter of hours, which is extremely helpful in trauma emergencies where time is of the essence. This flexibility may eventually democratize access to high-quality orthopaedic care in underserved areas. These advancements demonstrate that customization is no longer merely a luxury but is increasingly becoming a necessary component of the future of orthopaedic implants.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Personalized Surgery
One of the key characteristics of contemporary healthcare is the shift toward personalized medicine, and orthopaedics is no exception. The use of 3D-printed implants portends a time when medical interventions are tailored to the needs of individuals rather than groups.
As technology develops further, we can anticipate:
- Increased use of naturally dissolving bioresorbable materials after healing is finished.
- To develop smarter implants with embedded sensors, engineers, surgeons, and material scientists should work together more.
- Shorter surgery times as a result of improved accuracy and planning.
- Growth of prosthetics made with 3D printing that blend in perfectly with implants.
A new era is being shaped by all of these developments in the future of orthopaedic implants, increasing the efficiency, dependability, and accessibility of customized surgery.
Final Summary
3D-printed orthopaedic implants are actively changing how surgeries are carried out and how patients recover; they are no longer merely a sci-fi concept. The advantages are indisputable, ranging from quicker healing to precisely crafted implants. More patients will benefit from customized implants as costs come down and regulatory approval grows.
Leading the way in innovation, experts like Dr. Rakesh Mahajan at Mahajan Clinic are showing how medical knowledge and technology can work together to revolutionize patient care. The future of orthopaedic implants is clearly in the hands of 3D printing, precision, and personalization.